I could write a book about all the principles of argumentation that are found in Pride and Prejudice. But for now, here’s a few key rhetorical principles, a few of the Greek and Roman rhetoricians that turn me into a crazy Classical fan girl, and some other helpful links if you want to learn about rhetoric, the art of argument.
Classical Rhetoric Principles in Pride and Prejudice
The following are the rhetorical principles I mentioned in my Ignite Phoenix presentation. If you missed the presentation, I’ll be able to post it by the end of October.
- Confirmatio: the proof/reasons
- Refutatio: the counterargument
- Dicaelogia: admitting guilt but justifying your actions as necessary
- Apodioxis: a “chasing away” of concerns (rejecting false claims)
- Ethos: credibility
- Arete: virtue
- Quintilian: rhetoric is the art of the good citizen speaking well
- Aristotle: rhetoric is the use of “any available means of persuasion”
Here’s another version of it, in bookmark form:
Arrangement of a Classical Oration

(Adapted from Gideon Burton’s Silva Rhetoricae — on the left side, click on Arrangement for more details)
At the very bottom of this page, I’ve included a full breakdown of Mr. Collins’ proposal, using the arrangement of a classical oration.
My Favorite Greeks and Romans
Gorgias
Gorgias was a Sophist. I say the word Sophist the same way you might say the word Lawyer–the Sophists were persuasive and powerful, and yet can we really trust them?
Gorgias was said to be so persuasive that he convinced a foreign city-state to build a gold statue of him in one of their temples. Now that is argument at its finest.
One of his famous speeches is called the Encomium of Helen.
He has a great quote on the power of discourse, which I feel applies to rhetoric generally:
The power of discourse stands in the same relation to the soul’s organization as the pharmacopoeia does to the physiology of bodies. For just as different drugs draw off different humors from the body, and some put an end to disease and others to life, so too of discourses: some give pain, others delight, others terrify, others rouse the hearers to courage, and yet others by a certain vile persuasion drug and trick the soul.Aristotle
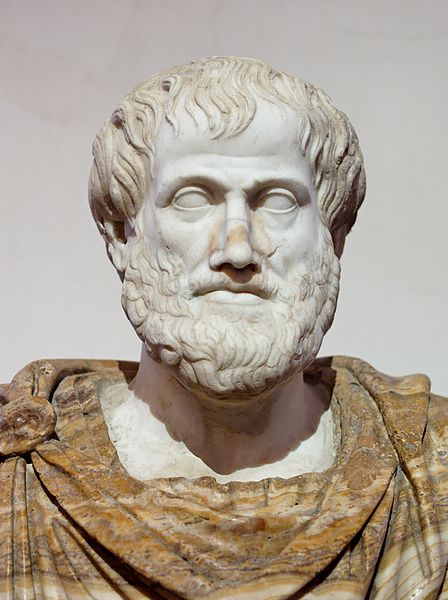
Public Domain imageThe famous Greek philosopher Aristotle wrote about everything, from biology to physics to government. And he basically founded the field of rhetoric.
On Rhetoric is actually a collection of lecture notes. What amazes me is that most of the rhetorical principles used by rhetoric scholars today can be found in some form or another in Aristotle work. If it’s not broken, don’t fix it.
The best translation of Aristotle’s On Rhetoric is by George Kennedy, though you can find other, older translations in the public domain.
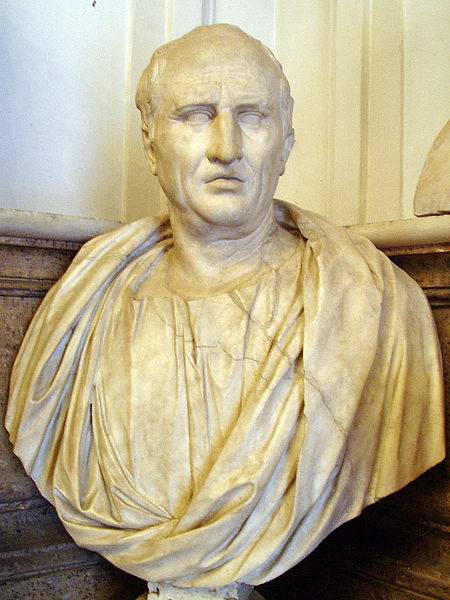
Cicero
Image Credit: Glauco92, Creative Commons license
You probably know Cicero for things other than rhetoric. He was a politician, a lawyer, and a philosopher. He was also a great orator, and he wrote about the art of rhetoric.
Cicero’s famous books on rhetoric are De Inventione and De Oratore.
In De Oratore Cicero writes:
“For purposes of persuasion the art of speaking relies wholly upon three things: the proof of our allegations, the winning of our hearers’ favor, and the rousing of their feelings to whatever impulse our case may require.”
For Cicero there are two objectives in rhetotic: “what to say” and “how to say it.”
Also, if you find yourself in ancient Rome and want to insult someone using an insult Cicero used in De Oratore, call that person a “clumsy Greekling.”
Other Helpful Rhetoric Sites and Books
- Silva Rhetoricae — this is a “forest” filled with classical rhetorical principles and approaches, put together by my friend Gideon Burton. It’s the most comprehensive, online resource on classical rhetoric that I’ve found.
- The History and Theory of Rhetoric by James A. Herrick — this is a great book that will introduce you to the major rhetoricians and theories.
Mr. Collins’ Proposal
Image by C.E. Brock, from Molland’s.
Here’s the full breakdown of Mr. Collins’ proposal using the arrangement of a classical oration:
1. Exordium (Introduction)
“You can hardly doubt the purport of my discourse, however your natural delicacy may lead you to dissemble; my attentions have been too marked to be mistaken.”
2. Narratio (Narrative)
“Almost as soon as I entered the house, I singled you out as the companion of my future life.”
3. Partitio (Outline)
“But before I am run away with by my feelings on the subject, perhaps it would be advisable for me to state my reasons for marrying–and, moreover, for coming into Hertfordshire with the design of selecting a wife, as I certainly did.”
4. Confirmatio (Proof/Reasons)
“My reasons for marrying are, first, that I think it a right thing for every clergyman in easy circumstances (like myself) to set the example of matrimony in his parish; secondly, that I am convinced that it will add very greatly to my happiness; and thirdly—which perhaps I ought to have mentioned earlier, that it is the particular advice and recommendation of the very noble lady whom I have the honour of calling patroness. Twice has she condescended to give me her opinion (unasked too!) on this subject; and it was but the very Saturday night before I left Hunsford—between our pools at quadrille, while Mrs. Jenkinson was arranging Miss de Bourgh’s footstool, that she said, ‘Mr. Collins, you must marry. A clergyman like you must marry. Choose properly, choose a gentlewoman for my sake; and for your own, let her be an active, useful sort of person, not brought up high, but able to make a small income go a good way. This is my advice. Find such a woman as soon as you can, bring her to Hunsford, and I will visit her.’ Allow me, by the way, to observe, my fair cousin, that I do not reckon the notice and kindness of Lady Catherine de Bourgh as among the least of the advantages in my power to offer. You will find her manners beyond anything I can describe; and your wit and vivacity, I think, must be acceptable to her, especially when tempered with the silence and respect which her rank will inevitably excite. Thus much for my general intention in favour of matrimony; it remains to be told why my views were directed towards Longbourn instead of my own neighbourhood, where I can assure you there are many amiable young women. But the fact is, that being, as I am, to inherit this estate after the death of your honoured father (who, however, may live many years longer), I could not satisfy myself without resolving to choose a wife from among his daughters, that the loss to them might be as little as possible, when the melancholy event takes place—which, however, as I have already said, may not be for several years. This has been my motive, my fair cousin, and I flatter myself it will not sink me in your esteem. And now nothing remains for me but to assure you in the most animated language of the violence of my affection. To fortune I am perfectly indifferent, and shall make no demand of that nature on your father, since I am well aware that it could not be complied with; and that one thousand pounds in the four per cents, which will not be yours till after your mother’s decease, is all that you may ever be entitled to. On that head, therefore, I shall be uniformly silent; and you may assure yourself that no ungenerous reproach shall ever pass my lips when we are married.”
5. Refutatio (Refutation)
Elizabeth then interrupts Mr. Collins, beginning the counterargument:
“You are too hasty, sir,” she cried. “You forget that I have made no answer. Let me do it without further loss of time. Accept my thanks for the compliment you are paying me. I am very sensible of the honour of your proposals, but it is impossible for me to do otherwise than to decline them.”
“I am not now to learn,” replied Mr. Collins, with a formal wave of the hand, “that it is usual with young ladies to reject the addresses of the man whom they secretly mean to accept, when he first applies for their favour; and that sometimes the refusal is repeated a second, or even a third time. I am therefore by no means discouraged by what you have just said, and shall hope to lead you to the altar ere long.”
“Upon my word, sir,” cried Elizabeth, “your hope is a rather extraordinary one after my declaration. I do assure you that I am not one of those young ladies (if such young ladies there are) who are so daring as to risk their happiness on the chance of being asked a second time. I am perfectly serious in my refusal. You could not make me happy, and I am convinced that I am the last woman in the world who could make you so. Nay, were your friend Lady Catherine to know me, I am persuaded she would find me in every respect ill qualified for the situation.”
“Were it certain that Lady Catherine would think so,” said Mr. Collins very gravely—”but I cannot imagine that her ladyship would at all disapprove of you. And you may be certain when I have the honour of seeing her again, I shall speak in the very highest terms of your modesty, economy, and other amiable qualification.”
“Indeed, Mr. Collins, all praise of me will be unnecessary. You must give me leave to judge for myself, and pay me the compliment of believing what I say. I wish you very happy and very rich, and by refusing your hand, do all in my power to prevent your being otherwise. In making me the offer, you must have satisfied the delicacy of your feelings with regard to my family, and may take possession of Longbourn estate whenever it falls, without any self-reproach. This matter may be considered, therefore, as finally settled.” And rising as she thus spoke, she would have quitted the room, had Mr. Collins not thus addressed her:
“When I do myself the honour of speaking to you next on the subject, I shall hope to receive a more favourable answer than you have now given me; though I am far from accusing you of cruelty at present, because I know it to be the established custom of your sex to reject a man on the first application, and perhaps you have even now said as much to encourage my suit as would be consistent with the true delicacy of the female character.”
“Really, Mr. Collins,” cried Elizabeth with some warmth, “you puzzle me exceedingly. If what I have hitherto said can appear to you in the form of encouragement, I know not how to express my refusal in such a way as to convince you of its being one.”
“You must give me leave to flatter myself, my dear cousin, that your refusal of my addresses is merely words of course. My reasons for believing it are briefly these: It does not appear to me that my hand is unworthy your acceptance, or that the establishment I can offer would be any other than highly desirable. My situation in life, my connections with the family of de Bourgh, and my relationship to your own, are circumstances highly in my favour; and you should take it into further consideration, that in spite of your manifold attractions, it is by no means certain that another offer of marriage may ever be made you. Your portion is unhappily so small that it will in all likelihood undo the effects of your loveliness and amiable qualifications. As I must therefore conclude that you are not serious in your rejection of me, I shall choose to attribute it to your wish of increasing my love by suspense, according to the usual practice of elegant females.”
“I do assure you, sir, that I have no pretensions whatever to that kind of elegance which consists in tormenting a respectable man. I would rather be paid the compliment of being believed sincere. I thank you again and again for the honour you have done me in your proposals, but to accept them is absolutely impossible. My feelings in every respect forbid it. Can I speak plainer? Do not consider me now as an elegant female, intending to plague you, but as a rational creature, speaking the truth from her heart.”
6. Peroratio (Conclusion)
“You are uniformly charming!” cried he, with an air of awkward gallantry; “and I am persuaded that when sanctioned by the express authority of both your excellent parents, my proposals will not fail of being acceptable.”
Visit my other Jane Austen pages:
Header Images
Jane Austen Image: Public Domain, Wikimedia Commons; Aristotle Image Credit: Nick Thompson, Creative Commons license